
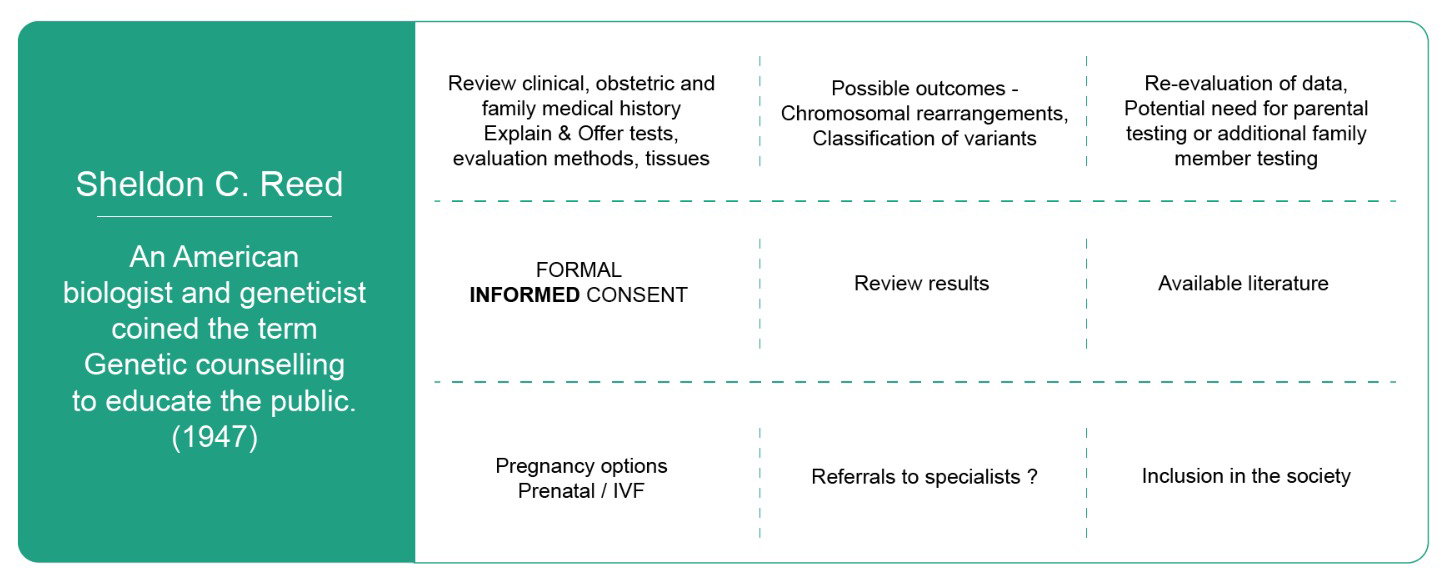
Carrier Screening: Identifies a person carrying one copy of a gene mutation. It is offered to someone with a family history of a disorder or belongs to a particular ethnic group which is prone to a specific disorder. The test can determine the inheritance risk to the progeny.
Predictive screening: Detects gene mutations associated with adult genetic disorders present in the family. Patient may be asymptomatic at the time of testing, but his susceptibility can be found out and decisions about lifestyle amendments and management / medication can be made.
Prenatal screening: Suggests likely changes in genetic meterial. Needs a confirmatory test before any irreversible action.
Pre-implantation screening: comprises a group of genetic assays used to evaluate embryos before transfer to the uterus.
New-born screening: performed within 24-48 hours of birth to 6 months of age. Detects many conditions allowing treatments / interventions to prevent severe irreversible disability including mental sub normalcy or even death.
It can confirm the said disorder. It helps making choices about treatment and care. It may need parental testing to determine inheritance risk to progeny. Other family members can decide if they want to be tested too.
Disclaimer: The website is not intended to be a substitute for the medical advice of a physician/ geneticist.
for diagnosis or treatment of any medical or genetic condition or drug/supplement intake, consult a physician.